Tags
Exercise is an effective treatment for depression: Study
Author
Author
- admin / 8 months

- 0
- 2 min read
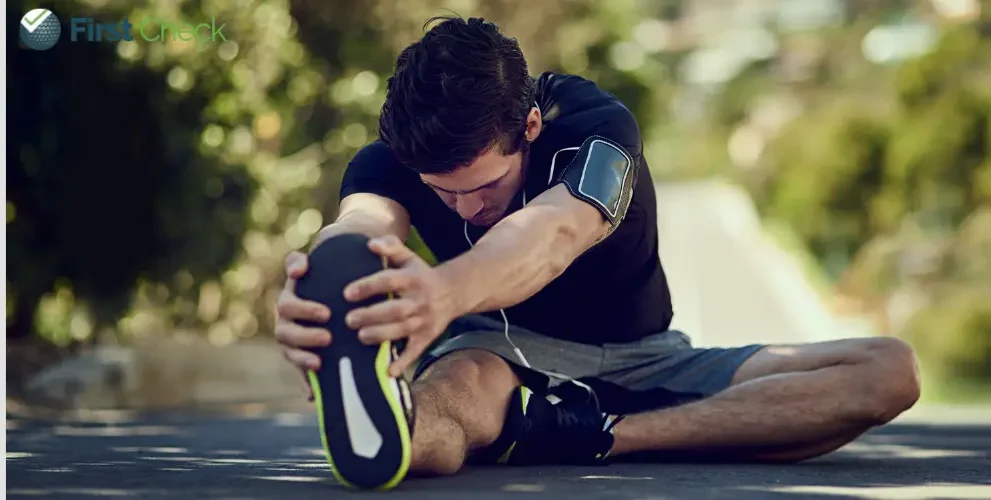

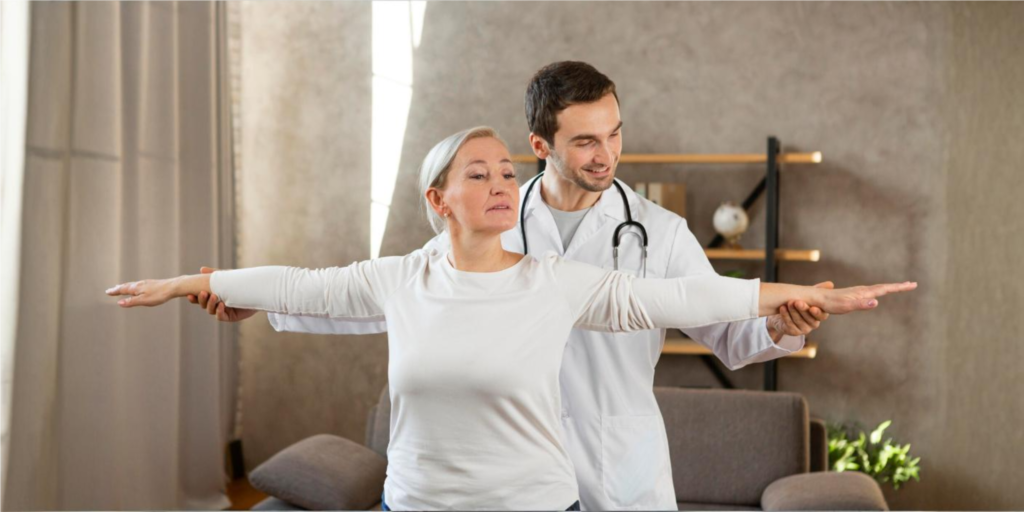
While walking or jogging benefited both genders, strength training was more beneficial for women, and yoga or qigong was more effective for men.
A recent study, published in the British Medical Journal, finds that exercise is an effective treatment for depression, with walking or jogging, yoga, and strength training more effective than other exercises, particularly when intense. The researchers note that these forms of exercise could be considered alongside psychotherapy and antidepressants as core treatments for depression.
Based on data from 14,170 participants across 218 studies, it was found that the impact of exercise on depression severity corresponded with the intensity of the prescribed regimen, showing heightened effectiveness particularly in group exercise settings and interventions featuring well-defined prescriptions.
The intensity of exercise prescribed was found to correlate with its benefits, with vigorous activity yielding better results. These benefits were consistent across different weekly doses, various comorbidities, and different baseline levels of depression.
The study identified walking or jogging, yoga, strength training, and dancing as the most effective exercise modalities. While walking or jogging benefited both genders, strength training was more effective for women, and yoga or qigong was more effective for men. Incidentally, yoga showed enhanced effectiveness among older adults, whereas strength training was more beneficial for younger individuals.
A combination of factors, such as social interaction, mindfulness, increased self-efficacy, immersion in green spaces, and neurobiological mechanisms can contribute to the outcomes of exercise on depression. While some exercise modalities directly promote mindfulness or social interaction, others are more conducive to acute adaptations that enhance self-efficacy, note the researchers.
The study emphasises the importance of personalised exercise prescriptions and a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of exercise on depression. Given that depression ranks as a significant contributor to disability worldwide, it would be prudent to include exercise as a complementary approach, alongside primary treatments like pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy.
Read More: Explainer: What is postpartum depression?