Researchers find strong association between consumption of ultra-processed foods and heightened risk of heart disease-related deaths, type 2 diabetes, obesity, anxiety, depression, sleep problems.
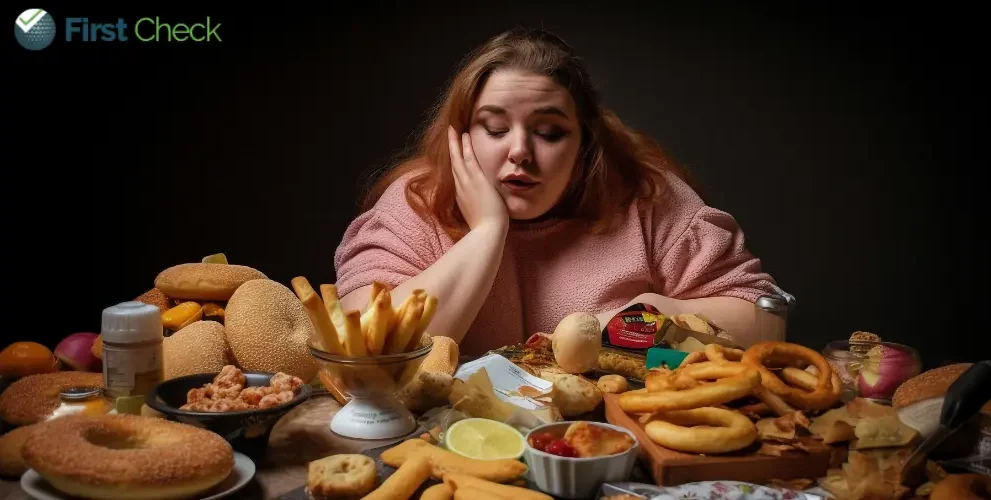
A recent study published in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) has unveiled a disconcerting association between the consumption of ultra-processed foods and heightened risk of heart disease-related deaths, type 2 diabetes, obesity, anxiety, depression, sleep problems, and an elevated risk of death from all causes. The meta-analysis gathered data from various studies to shed light on the extensive impact of these commonly consumed items, such as packaged snacks, carbonated soft drinks, instant noodles, and ready-made meals.
As the most comprehensive study on the subject till date, the study offers valuable insights:
- Researchers found that diets rich in ultra-processed foods were associated with a 44 per cent greater risk of depression and 48 per cent higher risk of anxiety. The impact was observed with the consumption of just 33 per cent of daily calories from ultra-processed foods.
- Taking in as little as 20 per cent of calories from these foods correlated with a 28 per cent faster rate of cognitive decline compared to those consuming less processed food.
- Researchers found a 25 per cent increase in the risk of dementia for every 10 per cent rise in ultra-processed food intake.
- While the exact cause-and-effect relationship remains uncertain, the evidence suggests that high consumption of these foods may elevate the risk of depression in the future.
- Additives present in ultra-processed foods, such as certain artificial sweeteners and monosodium glutamate, may interfere with the production and release of crucial brain chemicals, affecting mental and emotional well-being.
It is well-known that excessive intake of salt, sugar, and saturated fats is linked to chronic inflammation, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. However, it is less known that these conditions can significantly impact the brain, raising the risk of vascular dementia due to decreased blood flow to the brain.
Experts have likened ultra-processed foods to cigarettes, emphasising their potential addictiveness. The study underlines the need for public awareness regarding the health risks associated with a diet high in ultra-processed foods and emphasises the importance of making informed dietary choices for long-term health and well-being.
Read More : Fact-check: DIY Vagus nerve massage can’t cure mental health issues